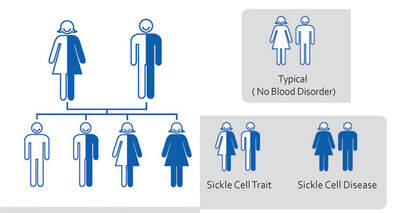
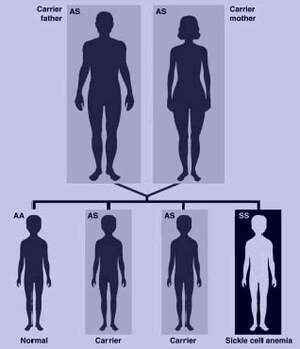
WHAT IS .SCT (Sickle Cell Trait)
|
|
|
“Having the sickle cell trait does not exclude an athlete from participating in sports, however, the training staff and coaches need to take precautions to ensure the athlete is not put in dangerous situations.” ~Geno Atkins, Cincinnati Bengals National Football League
|
SCT AND THE ATHLETE .Some people with SCT have been shown to be more likely than those without SCT to experience heat stroke and muscle breakdown when doing intense exercise, such as competitive sports or military training under unfavorable temperatures( very high or low) or conditions. Studies have shown that the chance of this problem can be reduced by avoiding dehydration and getting too hot during training. People with SCT who participate in competitive or team sports (i.e. student athletes) should be careful when doing training or conditioning activities. To prevent illness it is important to:
|
|
RECOMMENDATIONS ON SCREENING OF STUDENT ATHLETES FOR SCT: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns and Children (SACHDNC) to the Secretary, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services on Screening of Student Athletes for Sickle Cell Trait Source: www.cdc.gov
|
SCT SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Most people with sickle cell trait have no symptoms and will not have any health complications. Occasionally people with sickle cell trait can have blood in their urine. Under extreme conditions such as high altitude, severe dehydration, or very high intensity physical activity, red cells can become deformed or sickled.
|
SICKLE CELL TRAIT- EXERTIONAL SICKLING IN ATHLETES: Complications include muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), reduced blood supply to the spleen (ischemia/infarction), or increased pressure in the eye (glaucoma) following eye injuries. Finally, a very rare form of kidney cancer (renal medullary carcinoma) has been associated with sickle cell trait.
Source: www.hematology.org |
WHAT.What Causes Sickle Cell
WHO.Who is affected by Sickle Cell Disease
|